In a world where every click, scroll, and search is monitored, digital privacy is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity. Especially for students stepping into the world of tech, business, or finance, understanding how platforms like Google Chrome track your behavior is the first step toward becoming a responsible digital citizen.
Chrome is fast, convenient, and packed with features—but it also collects massive amounts of user data. From your browsing history and saved passwords to cookies and location tracking, Chrome uses this information for personalized ads, content suggestions, and more.
So the real question is, “Can you use Chrome without giving away your entire digital footprint?”
Absolutely. Here’s how.
Why Chrome Tracks You?
Before we dive into the how, let’s understand the why.
Google, the parent company of Chrome, makes most of its revenue through advertising. To optimize this, Chrome collects:
- Your browsing history (what websites you visit and when)
- Search terms typed in the address bar
- Cookies and site data to remember login info and track user behavior
- Location data for local search suggestions
- Auto-fill data like passwords and payment details
This may help with convenience—but it also raises concerns over who controls your data.
How to Stop Chrome From Tracking You?
1. Turn Off Sync
Chrome’s sync feature allows your activity across devices to be stored on Google servers.
How to disable it:
- Click the three-dot menu (top right corner)
- Go to Settings > You and Google > Sync and Google services
- Turn Sync off
Pro Tip: You can also choose what to sync—like disabling only browsing history or passwords.
2. Block Third-Party Cookies
Cookies help websites remember you—but third-party cookies track you across different sites.
How to block:
- Go to Settings > Privacy and Security > Cookies and other site data
- Choose Block third-party cookies
This will reduce personalized ad tracking significantly.
3. Turn Off Location Tracking
Location data can be precise—and intrusive.
How to disable:
- Settings > Privacy and Security > Site Settings > Location
- Choose Don’t allow sites to see your location
This keeps your location private unless you give explicit permission.
4. Clear Browsing Data Regularly
Cookies, cached files, and saved site data build up over time. Clear them often.
How to do it:
- Ctrl + Shift + Delete (Windows) or Command + Shift + Delete (Mac)
- Choose a time range (we recommend “All Time”) and clear cached images, cookies, and browsing history.
5. Use Privacy-Focused Extensions
Add-ons like Privacy Badger, uBlock Origin, or HTTPS Everywhere can limit how much you’re tracked while browsing.
Be cautious while installing extensions—only use those from trusted developers.
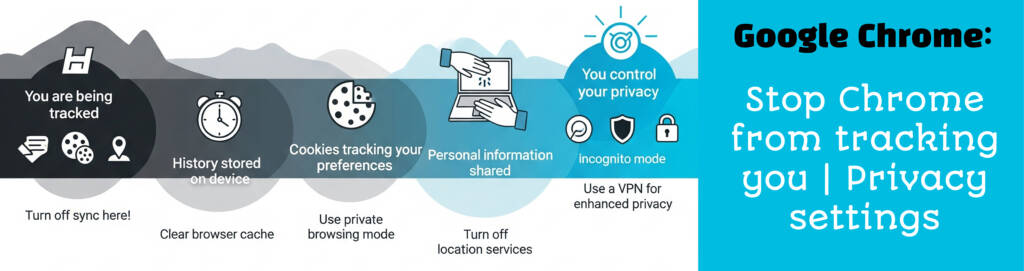
Bonus: Use Incognito Mode Wisely
While Incognito mode doesn’t save your browsing history or cookies, it doesn’t make you invisible. Your internet service provider, employer, or school can still track your activity. It’s useful for quick sessions where you don’t want your activity saved, but not a long-term privacy solution.
Final Thoughts: Privacy Is a Superpower
As future-ready students navigating tech, marketing, and finance careers, it’s vital to understand how tools like Chrome work behind the scenes. Whether you’re coding a full-stack app, launching a startup, analyzing data, or designing a digital campaign, data awareness gives you an edge.
Controlling your online footprint isn’t just about protecting yourself—it’s about building digital habits that align with ethical, informed, and secure professional practices.
Empower your skills and future-proof your career with real-world learning at FACE Prep Campus—where privacy, tech, and innovation meet.
FAQs
1. If I disable cookies, will websites stop working?
A: Some websites may not function properly without cookies, especially those requiring login. You can allow cookies for specific sites if needed.
2. Can Google still track me if I log into Gmail or YouTube?
A: Yes. If you’re logged into a Google account, your activity can still be tracked—even with some privacy settings enabled. Consider using different browsers for different tasks.
3. What about Google’s Privacy Sandbox?
A: Privacy Sandbox is Google’s attempt to phase out third-party cookies with new tracking technologies like Topics API. While it’s meant to enhance privacy, it’s still under scrutiny for how much it truly limits data collection.